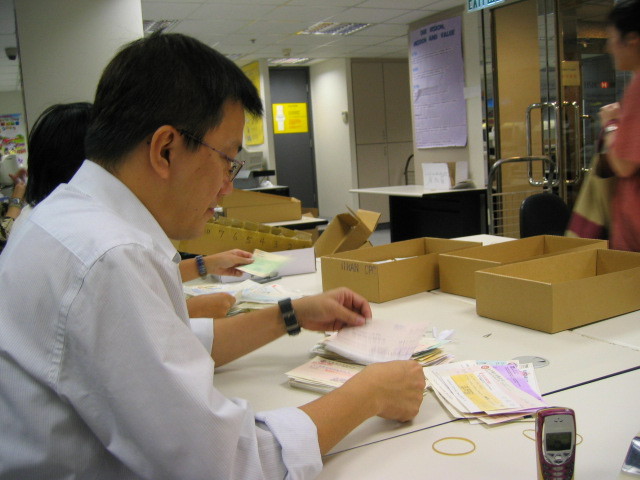
Under California Labor Code section 515.5, certain software industry employees are exempt from overtime pay requirements, if they perform specific, exempt duties and receive a rate of pay not less than the statutorily-specified rate.
Effective January 1, 2020, the computer software employee’s minimum hourly rate of pay, in order to be subject to this exemption, increases from $45.41 / hour to $46.55 / hour, the minimum monthly salary exemption will increase from $7,883.62 to $8,080.71, and the minimum annual salary exemption will increase from $94,603.25 to $96,968.33.
In order to be correctly classified as exempt from overtime under the California computer professional exemption, all of the requirements of section 515.5 must be met. Thus, for instance, an employee how is paid more than the above referenced minimum, but who performs work that lacks in creativity and independent judgment required by this law, as it’s often the case with IT administrators, will not qualify for this exemption and should be eligible for overtime pay, like any other non-exempt, hourly employee.
 San Francisco Employment Law Firm Blog
San Francisco Employment Law Firm Blog



 The Harris court, applying this analysis, found that insurance adjusters, who sued the defendant for unpaid overtime, were primarily engaged in “production” – adjusting individual claims for their employer. They investigate claims, make coverage determination, set reserves, negotiate settlements, make settlement recommendations for claims beyond their settlement authority, identify potential fraud, and so forth. Noe of that work was found to be carried out at the level of management policy or general operations. Rather, it is all part of the day-to-day operation of defendants’ business.
The Harris court, applying this analysis, found that insurance adjusters, who sued the defendant for unpaid overtime, were primarily engaged in “production” – adjusting individual claims for their employer. They investigate claims, make coverage determination, set reserves, negotiate settlements, make settlement recommendations for claims beyond their settlement authority, identify potential fraud, and so forth. Noe of that work was found to be carried out at the level of management policy or general operations. Rather, it is all part of the day-to-day operation of defendants’ business. 